Native to the American continent, sweet potatoes (Ipomoea batatas) are nutritious vegetables with many incredible properties and health benefits. Sweet potatoes come in a variety of colors, their flesh ranging from white to beige, yellow, orange and brown red, even purplish. The darker the colour of the flesh, the moister and sweeter the potato and the higher its antioxidant content. Each color is indicative of a different antioxidant, so know you are getting good nutrition from all varieties of sweet potato.
Interesting enough, the root is not the only edible part of sweet potatoes: in many African countries, the leaves are an important part of people’s diet as well. Overall, the sweet variant is not only healthier than regular potatoes, but also more flavorful compared to many other vegetables, which significantly increases its popularity among people of all ages.

What are sweet potatoes?
Sweet potatoes are very distant ‘relatives’ of the common potato. They boast a moderate nutritional value that surpasses slightly that of regular potatoes. Their incredibly diverse natural pigmentation is indicative of their rich carotenoid content, potent natural pigments which, among other things, promote a positive response to the hormone insulin. However, moderate consumption is advised, especially with diabetes. All diabetics must limit their intake of carbohydrates from food in order to maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
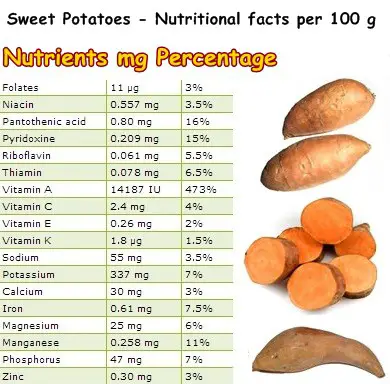
Nutrition facts and benefits of Sweet Potatoes
Also, carotenoids have incredible antioxidant properties which means they are excellent scavengers of free radicals. Studies conducted throughout the years have shown that a diet consisting of fruits and vegetables rich in carotenoids significantly reduces the risks of developing serious life-threatening diseases.
Remember: people (and animals) cannot synthesize carotenoids, thus it is imperative that we adapt our diet so to include nutritious foods such as sweet potatoes and other sources of the pigments.
Interesting fact: the overwhelmingly vivid colors of flamingos, lobsters and salmons are caused by a high concentration of carotenoid pigments. Similarly, certain foods such as carrots or sweet potatoes have such intense coloring because of their high carotenoid content, making the pigmented antioxidant compounds not only a source of health benefits, but also contributors to food attractiveness.

Sweet potatoes are especially rich in vitamin A and beta-carotene, a precursor of vitamin A. A little over 100 g of sweet potatoes is enough to meet our daily allowance of the nutrient. Why is vitamin A so important? Well, apart from maintaining healthy skin and mucous membranes, vitamin A, and beta-carotene, are pivotal for good vision.
Also, because of their excellent antioxidant properties, both nutrients protect our eyes from free radical damage produced by blue light. In time, this can lead to a serious condition called macular degeneration (loss of central vision). So remember, sweet potatoes are good for your eyesight too.
See also: Can You Eat Sweet Potato Skin?
Sweet potatoes contain vitamin C, an incredibly potent water-soluble, antioxidant vitamin. Besides being an efficient natural anti-inflammatory, vitamin C is required for the synthesis of collagen, the main structural protein in our body that ensures the integrity of our skin, internal organs, bones and blood vessels. Moreover, it helps the body develop resistance against viral infections by increasing the aggressiveness of white blood cells. Interesting fact: it is a common practice for doctors and nurses to get injections of 1 g (1000 mg) of vitamin C when they feel a cold lurking by. Their body reacts in no time and they don’t even let out a sneeze.
As an antioxidant, vitamin C efficiently neutralizes the damaging effects of free radicals. Have you ever wondered how some people seem to go through time unchanged? Their secret is this fountain of youth called vitamin C, which can be found in generous amounts in many fruits and vegetables such as strawberries, lemons, oranges, kiwi and sweet potatoes.
A recent study conducted on 2,000 individuals found that a diet rich in both beta-carotene and vitamin C, both of which can be found in sweet potatoes, significantly reduced their risks of developing prostate cancer. Another study conducted at Harvard Medical School showed that women who consumed foods rich in beta-carotene had a 25% lower risk of developing breast cancer. Eating sweet potatoes does seem like a smart move.
Sweet potatoes are a good source of potassium, an electrolyte known for its amazing cardiovascular benefits. When the temperatures sky rocket, potassium seems to ooze out of our flesh so it is extremely important to constantly replace what we lose. If you don’t feel like eating another banana (also rich in potassium), try a baked sweet potato and I guarantee you will no longer feel like your are about to faint and fall on the ground.
Of course, sweet potatoes have other important nutrients such as B-group vitamins, manganese, magnesium and phosphorus. Additionally, they contain good amounts of dietary fiber, an excellent natural remedy for constipation, known to also promote colon health. Dietary fiber can efficiently reduce the bad (LDL) cholesterol in our blood which leads to a healthy heart and healthy arteries.
Last but not least, sweet potatoes are starchy vegetables which means they contain a carbohydrate called starch. Vegetable starch is actually a quality carbohydrate, making sweet potatoes a great addition to a healthy, balanced and nutritious diet. Whether you like them baked, boiled, turned into soup, salad, as a side or main dish, they are an excellent source of vitamins, minerals and phytochemicals.
