A member of the Zingiber officinale family, ginger is a spice, medicinal herb and a highly prized food. It was first cultivated in Asia, but spice trade facilitated its spread to the farthest corners of the world.
Nowadays, ginger is a very popular spice and many people strongly believe in its medicinal properties.
Whether you use it as powder or prefer the freshly picked root, ginger can be a wonderful addition to your diet, provided you can endure its unique spiciness.
What does ginger taste like?
Fresh ginger tends to have a milder, spicy-sweet taste whereas powder ginger tends to be much more pungent. Cooked ginger is soft in texture and only faintly pungent, with a fresh lemony flavor.
The chemical responsible for the spiciness of ginger is called gingerol and preliminary studies suggest that it can efficiently lower blood pressure and may even be used for the treatment of several forms of cancer.
Interesting enough, ginger roots have a curvature that slightly resembles the shape of a stomach. Maybe this is nature’s subtle way of indicating what the best uses of ginger root are.
See also: Can You Eat Raw Ginger?

What is ginger good for?
Traditionally, ginger was used to treat any ailment related to the stomach area. Stomach pain, nausea, constipation, stomach bugs were all treated by either consuming a bit of ginger root or drinking ginger tea or special infusions. Modern medicine also supports these claims advanced by traditional medicine: it has been proven that ginger efficiently stimulates the production of bile, and thus aids digestion. Moreover, because it supports the digestion process, ginger greatly improves the absorption of nutrients at the intestinal level.
In addition to this, it is a strong, natural antiemetic that can help ease nausea and prevent emesis or vomiting. It has proved incredibly efficient in reducing nausea caused by both pregnancy and chemotherapy. In infectious gastroenteritis, it prevents or reduces vomiting frequency and further dehydration by helping manage nausea. Ginger can be used raw, fresh or dried, as such or in tea and other preparations for treating nausea.
Ginger is a potent antimicrobial which can efficiently treat intestinal infections. It can even help prevent and treat gastritis caused by the dreaded Helicobacter pylori and thus significantly reduce the risk of developing an ulcer, but only when used cautiously. Ginger is also a great remedy for diarrheal disease caused by viral infectious agents: while it does not treat the infection itself, its various therapeutic properties (such as nausea management) are conducive to good health by supporting recovery.

However, those with existing digestive conditions such as gastritis, ulcers or acid reflux may also experience side effects if they eat too much ginger or even small amounts of it, depending on the severity of their digestive conditions. The same compounds responsible for the health benefits of ginger have been found to act as irritants on sensitive mucous linings and cause inflammation and pain. Ginger is thus bad for gastritis, acid reflux and even hemorrhoids, worsening symptoms and the conditions themselves.
See more foods to eat and to avoid for gastritis.
As a prevention method or a healthy practice, you can drink a cup o ginger tea mixed with chamomile and lemon balm every night or more infrequently, sometime before going to bed. Not only will it contribute to your good health, but you will also feel relaxed and enjoy a good rest. Alternatively, you can add ginger to everyday dishes such as rice or fish to make them more savory and enjoy some of the therapeutic properties of the spicy root.
However, remember to always eat ginger in moderation because excessive intakes can prove harmful. For instance spicy ginger can, in rare instances, cause allergic reactions with the potential for anaphylactic shock. And the ingestion of excessive amounts may lead to nausea, vomiting, bloating, heartburn, severe indigestion or worsen symptoms of gastritis, stomach ulcers or gallbladder problems as well as hemorrhoids. Therefore, in order to enjoy all of the amazing health benefits of ginger, it should be consumed in reasonable limits.
Also see these 7 reasons not to eat ginger.
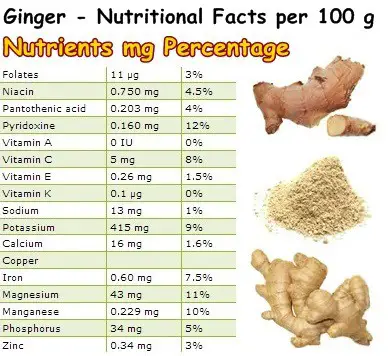
Although ginger appears to have a moderate vitamin and mineral content, it is an incredible source of phytochemicals, enzymes and amino acids. It is great for blood circulation because it prevents clotting and efficiently lowers high blood pressure. Also, a regular consumption is said to lower the risk oh heart attack, angina pectoris and thrombosis (blood clots). In addition to this, ginger can alleviate a vast number of stomach problems from diarrhea to aches, pain, nausea, vomiting and even infections.
What are the side effects of Ginger?
Digestive upset.
If you have raw or dried ginger, it’s possible to experience digestive upset with symptoms such as indigestion, acid reflux, heartburn, a bad taste in the mouth, nausea, vomiting, bloating, cramps and stomach pain, and even diarrhea. The more ginger you have at once and the more frequently you have it, the more likely the side effects. People with existing digestive conditions such as gastritis or GERD are more likely to experience side effects as a result of eating ginger.
Allergic reactions
Ginger can be a source of allergic reactions in which case it should be avoided in all forms and preparations. If you experience a rash, tingling of the lips or tingling in the throat, swelling of the lips, tongue or throat, wheezing, difficulty breathing, dizziness, low blood pressure, a fainting sensation or severe digestive distress, know that these are symptoms of an allergic reaction and you need to seek medical help immediately before your condition deteriorates and you develop anaphylactic shock.
Bowel obstruction
While you can drink ginger tea, add a pinch of ginger powder to a dish or eat a small piece of cooked ginger without any issues, it’s important to avoid consuming too much of the root at once. Just as important, if it’s ginger root that you’re eating, make sure you chew it well. A single piece of poorly chewed ginger root can cause bowel obstruction. This is a rare side effect, but worth mentioning nonetheless. Aside from this, the spice can be a great addition to your diet and give an unbelievable boost to your health.
