We often see them on bagels, bread or in cakes and wonder what’s the purpose of those small, dark seeds that just get stuck into our teeth. As it happens, poppy seeds are an incredibly rich source of minerals and vitamins and boast impressive antioxidant properties. Around 100 g of poppy seeds supply our body with 87% of the Recommended Daily Intake of magnesium, 72% zinc, 122% iron, 144% calcium and so on. Imagine strong bones and teeth, great energy levels, wrinkle-free skin, a healthy heart and thyroid gland, good immunity and fewer gray hairs.
These are but a few of the health benefits of poppy seeds. Edible poppy seeds come from a variety of poppy called Papaver somniferum. As its scientific name suggests, this poppy variety has some other impressive uses besides nourishing the body. Poppy seeds are used to extract a strong pain-reliever and sedative used for pharmaceuticals preparation. The medicinal agent is made from a natural rubbery substance exuded by the unripe pods of the plant.

Modern medicine uses immature poppy seed pods to extract a strong analgesic and sedative for the purpose of producing morphine and codeine, two major pain-relievers used to alleviate pain in cancer patients, treat hypertension, depression, relieve labor pains and manage chronic pain. The incredible analgesic properties of poppy were known even in ancient times when doctors used unripe poppy pods to perform rudimentary surgeries. Along with the development of trade, poppy flowers have come to be cultivated throughout the world. The plant requires generous sun exposure and a fertile soil to thrive. Although poppy flowers are symbolically depicted as being red, they actually come in a variety of colors such as white, yellow, orange, red, blue and purple.
Although unripe poppy pods ooze medicinal compounds when cut, the concentration of such compounds in ripe, edible poppy seeds is too low to produce any visible alterations of consciousness or sedative effects, in amounts normally provided by dietary intake. And since the rubber is not extracted into oil, poppy seed oil contains even less medicinal agents than the whole seeds. Both poppy seeds and poppy seed oil are considered to be two of the healthiest ‘foods’ on the planet.
Fatty acids in poppy seeds
Fatty acids profile and content of poppy seeds oil:
Poppy seeds are about 40% fatty acids and volatile essential oils. They are particularly rich in Omega-6 fatty acids, contain small amounts of Omega-9 and saturated fats. Linoleic acid is a polyunsaturated Omega-6 fatty acid and accounts for 65 to 75% of the total fatty acids compositions of poppy seeds oil. Oleic acid is a monounsaturated Omega-9 fatty acid and represents between 13 and 21% of the total fatty acids profile. Lastly, the saturated fats in poppy seeds oil are in the form of palmitic acid and represent 8.5 to 10% of the total fatty acids composition (source: Fatty acid composition and some bioactive properties of edible oil extracted from different varieties of poppy (Papaver somniferum L.) seeds). Some sources say the seeds provide negligible amounts of Omega-3 fatty acids.

Poppy seeds benefits and uses
Research shows a generous, but not excessive intake of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids such as those from poppy seeds, with a ratio of 4:1 or 3:1 Omega-3 to Omega-6 fatty acids, representative of the Mediterranean diet, favors a healthy blood lipid profile and promotes cardiovascular health, leading to a reduced risk of stroke and coronary heart disease. Both linoleic and oleic acid help lower LDL cholesterol levels and increase HDL (good) cholesterol levels. More recent research further shows saturated fats such as palmitic acid do not raise blood cholesterol levels, when consumed in limited amounts.
Pure poppy seed extract is widely used for the preparation of cough syrups, mucus-thinning expectorants and analgesics, due to the plant’s potent sedative effects which allow for recovery of the affected mucous membranes and promote healing. Nonetheless, eating a tablespoon of poppy seeds is not reported to produce health effects of this magnitude, alter normal brain function or induce highly euphoric states. Instead, it will supply you with important amounts of vitamins, minerals and antioxidants.
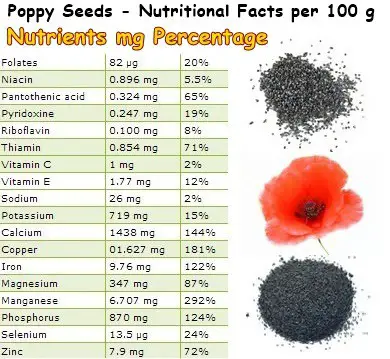
About 100 g of poppy seeds contains 65% of the RDI (recommended daily intake) of pantothenic acid, or vitamin B5, a great ally in coping with stress. Also, poppy seeds provide 71% of the RDI of thiamine or vitamin B1, as well as 20% of the RDI of folic acid. While thiamine boosts energy, folic acid is especially recommended during the preconception period and pregnancy to ensure the birth of a healthy baby. Vitamin E, also found in generous amounts in the seeds (12% of RDI), promotes skin health, nourishing skin cells and helping them retain moisture, for a more plump and healthy appearance. It also helps preserve cell membrane integrity, exerting antioxidant effects and anti-aging benefits.
Poppy seeds are especially good for the heart. In addition to healthy fatty acids, they contain magnesium (87%) and potassium (15%). These two minerals regulate blood pressure, heart rate, body fluids, prevent palpitations, high blood pressure and extrasystoles. If you are suffering from any form of heart disease, it is important to have a healthy dietary supply of both potassium and magnesium.
Poppy seeds are a rich source of dietary iron (122%) and are a great food for preventing and treating anemia caused by iron-deficiency. Because of their incredible zinc content (72%), they provide great support to our immune system and help prevent respiratory infections such as colds.
Selenium (24%) regulates thyroid activity and, consequently, balances hormones. The thyroid gland is famous for making weight fluctuate and inducing metabolic disorders, so eating selenium (and iodine) rich foods is crucial for preserving thyroid health. Both iodine and selenium deficiency are major causes of hypothyroidism, or underactive thyroid.
Phosphorus (124%) is physically part of our bones and teeth and accounts for bone strength as well as the hormonal processes that trigger bone dissolving followed by bone formation for stronger, healthier bones. Last but not least, poppy seeds contain incredible amounts of manganese (292%), a powerful antioxidant-mineral, as well as copper (181%), a powerful antibacterial and anti-aging agent. Eating copper-rich poppy seeds delays hair graying and eye discoloring. All of the nutritional variety of poppy seeds has a tonic action and helps combat the side effects of stress.
Conclusion
Poppy seeds are one of those foods that are best eaten in moderation. And while a limited intake limits vitamin, mineral and antioxidant intake too, there will still be benefits to eating smaller amounts of the seeds. A popular recipe includes ground poppy seeds made into a paste and added to curries or desserts for a unique flavor. Another great combination is poppy seed paste and coconut flakes for caked and sweets. My favorite is a dessert cake with poppy seeds dough, vanilla cream and chocolate-topped oats biscuits. The seeds make a great bread topping and are wonderful on bagels or in salads in combination with other seeds or nuts, adding to diet variety and health benefits.
